Comparison of azithromycin and a combination of trypsin, chymotrypsin and papain proteolytic enzymes for the treatment of bovine cutaneous papillomatosis
Main Article Content
Abstract
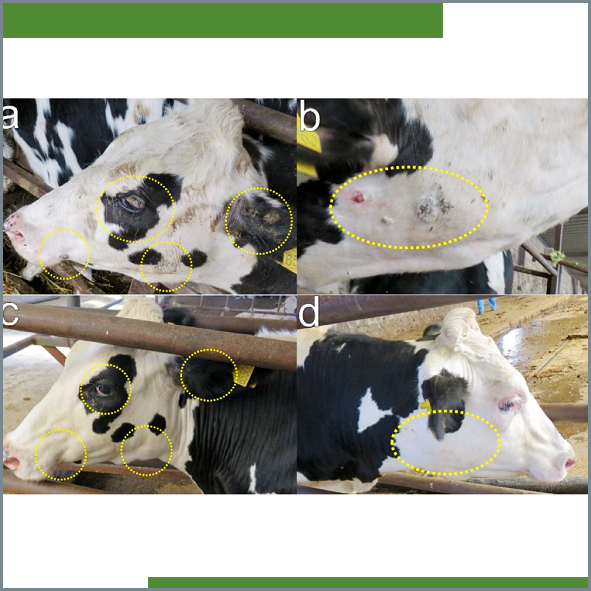
Although various methods have been used in the treatment of bovine cutaneous papillomatosis (BCP), no definite treatment has yet been established. There are no studies regarding the efficacy of azithromycin (AZ) and of any combination of trypsin, chymotrypsin, and papain proteolytic enzymes (PEC) in the treatment of BCP. The objective of this study was to investigate the efficacy of AZ and PEC in the treatment of BCP. A total of 24 female Holstein cattle of 6-17 months of age with spontaneous BCP were used for this study. In addition to the clinical findings, the diagnosis was confirmed with histopathological examinations. The animals were divided at random into three groups (n = 8). The AZ group received 10 mg/kg/day PO for 10 days. In the PEC group, an injectable suspension of proteolytic enzymes was applied IM at 0.4 mL/10 kg dose, 3 times with 8-10 days interval and the spray was used topically once a day for 10 days. The control group (CO) was not treated. The mean in papilloma warts decreased 92.4 % in the AZ group, 83.38 % in the PEC group, and 59.48 % in the CO. There were statistically significant differences in warts presence decreases between the three groups (P < 0.05). Both AZ and PEC were considered successful for the BCP treatment. However, AZ was found more effective than PEC.
Article Details
License

Veterinaria México OA by Facultad de Medicina Veterinaria y Zootecnia - Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Licence.
Based on a work at http://www.revistas.unam.mx
- All articles in Veterinaria México OA re published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Unported (CC-BY 4.0). With this license, authors retain copyright but allow any user to share, copy, distribute, transmit, adapt and make commercial use of the work, without needing to provide additional permission as long as appropriate attribution is made to the original author or source.
- By using this license, all Veterinaria México OAarticles meet or exceed all funder and institutional requirements for being considered Open Access.
- Authors cannot use copyrighted material within their article unless that material has also been made available under a similarly liberal license.