Comparison of azithromycin and a combination of trypsin, chymotrypsin and papain proteolytic enzymes for the treatment of bovine cutaneous papillomatosis
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
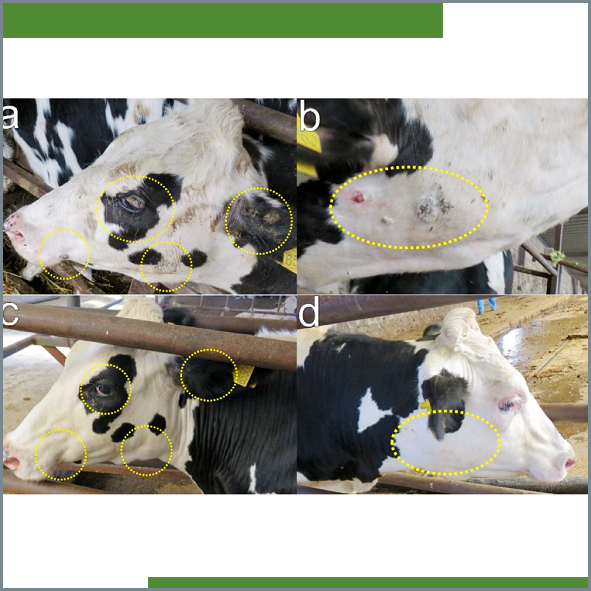
Although various methods have been used in the treatment of bovine cutaneous papillomatosis (BCP), no definite treatment has yet been established. There are no studies regarding the efficacy of azithromycin (AZ) and of any combination of trypsin, chymotrypsin, and papain proteolytic enzymes (PEC) in the treatment of BCP. The objective of this study was to investigate the efficacy of AZ and PEC in the treatment of BCP. A total of 24 female Holstein cattle of 6-17 months of age with spontaneous BCP were used for this study. In addition to the clinical findings, the diagnosis was confirmed with histopathological examinations. The animals were divided at random into three groups (n = 8). The AZ group received 10 mg/kg/day PO for 10 days. In the PEC group, an injectable suspension of proteolytic enzymes was applied IM at 0.4 mL/10 kg dose, 3 times with 8-10 days interval and the spray was used topically once a day for 10 days. The control group (CO) was not treated. The mean in papilloma warts decreased 92.4 % in the AZ group, 83.38 % in the PEC group, and 59.48 % in the CO. There were statistically significant differences in warts presence decreases between the three groups (P < 0.05). Both AZ and PEC were considered successful for the BCP treatment. However, AZ was found more effective than PEC.
Detalles del artículo
License

Veterinaria México OA por Facultad de Medicina Veterinaria y Zootecnia de la Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México se distribuye bajo una Licencia Creative Commons Atribución 4.0 Internacional.
Basada en una obra en http://www.revistas.unam.mx
- Todos los artículos en Veterinaria México OA se publican bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento 4.0 Unported (CC-BY 4.0). Con esta licencia, los autores retienen el derecho de autor, pero permiten a cualquier usuario compartir, copiar, distribuir, transmitir, adaptar y hacer uso comercial de la obra sin necesidad de proporcionar un permiso adicional, siempre y cuando se otorgue el debido reconocimiento al autor o fuente original.
- Al utilizar esta licencia, los artículos en Veterinaria México OA cubren o exceden todos los requisitos fundacionales e institucionales para ser considerados de Acceso Abierto.
- Los autores no pueden utilizar material protegido por derechos de autor en su artículo a menos que ese material esté también disponible bajo una licencia igualmente generosa.