Effect of resveratrol on the <em>in vitro</em> maturation of ovine (<em>Ovis aries</em>) oocytes and the subsequent development of handmade cloned embryos
Main Article Content
Abstract
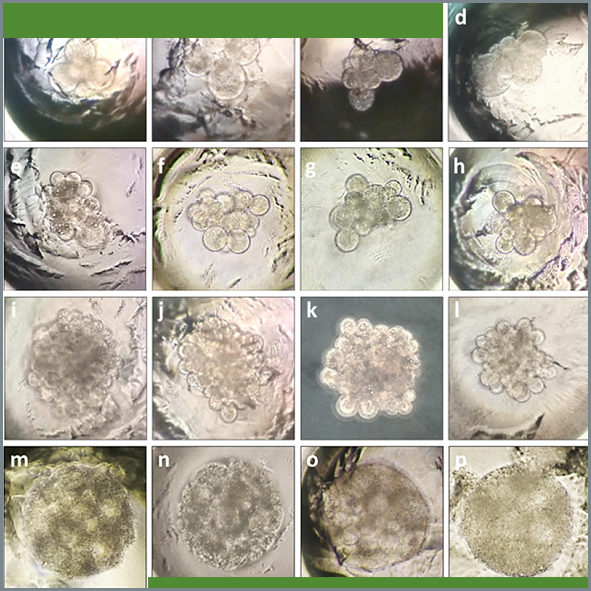
The effect of resveratrol on the in vitro maturation (IVM) of ovine (Ovis aries) oocytes and the development of handmade cloned embryos was evaluated. The nuclear maturation and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in the oocytes, as well as the early development and morphological cloned embryo quality, were evaluated under different resveratrol concentrations (0, 0.5, 2 and 5 μM). After IVM, no significant difference was observed in the maturation rate of oocytes treated with 0.5 μM (81.3 %) and 2 μM (72 %) resveratrol compared to that of the control group (0 μM) (74.2 %), but the rate significantly decreased at 5 μM (56 %) (p < 0.05). When the oocyte ROS levels were determined, no significant differences among the groups were observed (p > 0.05). For cloned embryo development, the embryos obtained from the oocytes treated with 0.5 μM resveratrol showed higher (p < 0.05) compacted morula rates (10.7 %) compared to the embryos obtained from the oocytes treated with 0, 2 and 5 μM (6.2, 0 and 0 %, respectively). Regarding embryo morphological quality, the embryos from the oocytes treated with 0.5 μM resveratrol showed a lower rate of poor quality morulae (4.7 %) in comparison to those treated with 0, 2 and 5 μM (23.8, 23.3 and 33.3 %, respectively) (p < 0.05). In conclusion, resveratrol showed no significant improvement on the IVM or ROS levels in domestic ovine oocytes. However, treatment with 0.5 μM resveratrol during IVM improved embryo quality and promoted morulae compaction of Ovis aries handmade cloned embryos.
Article Details
License

Veterinaria México OA by Facultad de Medicina Veterinaria y Zootecnia - Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Licence.
Based on a work at http://www.revistas.unam.mx
- All articles in Veterinaria México OA re published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Unported (CC-BY 4.0). With this license, authors retain copyright but allow any user to share, copy, distribute, transmit, adapt and make commercial use of the work, without needing to provide additional permission as long as appropriate attribution is made to the original author or source.
- By using this license, all Veterinaria México OAarticles meet or exceed all funder and institutional requirements for being considered Open Access.
- Authors cannot use copyrighted material within their article unless that material has also been made available under a similarly liberal license.