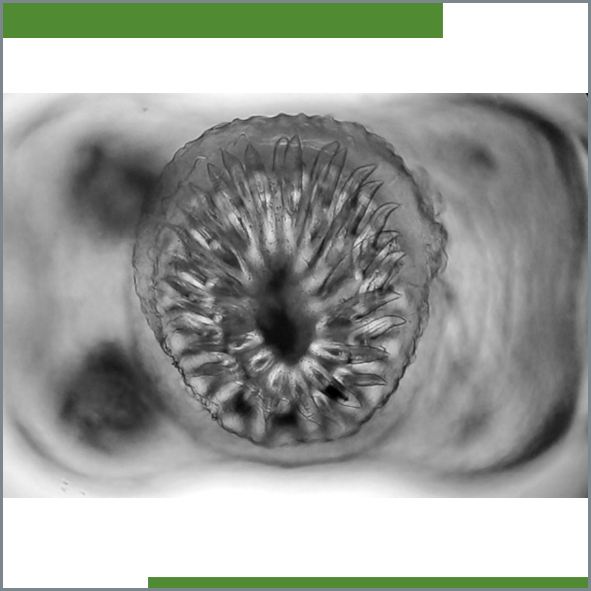
<em>Mycobacterium tuberculosis</em> and <em>Mycobacterium bovis</em> derived proteins induce caspase-independent apoptosis in bovine macrophages
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
Veterinaria México OA
ISSN: 2448-6760
Cite this as:
- Maciel-Rivera A, Flores-Villalva S, Jímenez-Vázquez I, Catalán-Barcenas O, Espitia-Pinzón CI, Morán J, Arriaga-Pizano L, Benítez-Guzmán A, Alfonseca-Silva E, Gutiérrez-Pabello JA. Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis derived proteins induce caspase-independent apoptosis in bovine macrophages. Veterinaria México OA. 2019;6(1). doi: 10.22201/fmvz.24486760e.2019.1.560.
Detalles del artículo
Citas
Michel AL, Muller B, van Helden PD. Mycobacterium bovis at the animal-human interface: a problem, or not? Veterinary microbiology. 2010;140(3-4):371-81. Epub 2009/09/24. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2009.08.029.
Caminiti A, Pelone F, LaTorre G, De Giusti M, Saulle R, Mannocci A, et al. Con¬trol and eradication of tuberculosis in cattle: a systematic review of economic evidence. The Veterinary record. 2016;179(3):70-5. Epub 2016/07/17. doi: 10.1136/vr.103616.
Sakamoto K. The pathology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infec¬tion. Veterinary pathology. 2012;49(3):423-39. Epub 2012/01/21. doi: 10.1177/0300985811429313.
Cassidy JP. The pathogenesis and pathology of bovine tuberculosis with insights from studies of tuberculosis in humans and laboratory animal models. Veteri¬nary microbiology. 2006;112(2-4):151-61. Epub 2005/11/29. doi: 10.1016/j. vetmic.2005.11.031.
Rohde K, Yates RM, Purdy GE, Russell DG. Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the environment within the phagosome. Immunological reviews. 2007;219:37-54. Epub 2007/09/14. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2007.00547.x.
Molloy A, Laochumroonvorapong P, Kaplan G. Apoptosis, but not necrosis, of in¬fected monocytes is coupled with killing of intracellular bacillus Calmette-Guer¬in. The Journal of experimental medicine. 1994;180(4):1499-509. Epub 1994/10/01.
Behar SM, Martin CJ, Booty MG, Nishimura T, Zhao X, Gan HX, et al. Apopto¬sis is an innate defense function of macrophages against Mycobacterium tu¬berculosis. Mucosal immunology. 2011;4(3):279-87. Epub 2011/02/11. doi: 10.1038/mi.2011.3.
Lee J, Hartman M, Kornfeld H. Macrophage Apoptosis in Tuberculosis. Yonsei Medical Journal. 2009;50(1):1-11. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.1.1.
Wu H, Che X, Zheng Q, Wu A, Pan K, Shao A, et al. Caspases: a molecular switch node in the crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. International journal of biological sciences. 2014;10(9):1072-83. Epub 2014/10/07. doi: 10.7150/ ijbs.9719.
Esquivel-Solis H, Vallecillo AJ, Benitez-Guzman A, Adams LG, Lopez-Vidal Y, Guti¬errez-Pabello JA. Nitric oxide not apoptosis mediates differential killing of Myco¬bacterium bovis in bovine macrophages. PloS one. 2013;8(5):e63464. Epub 2013/05/22. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063464.
Divangahi M, Behar SM, Remold H. Dying to live: how the death modality of the infected macrophage affects immunity to tuberculosis. Advances in ex¬perimental medicine and biology. 2013;783:103-20. Epub 2013/03/08. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-6111-1_6.
Chen M, Gan H, Remold HG. A mechanism of virulence: virulent Mycobacte¬rium tuberculosis strain H37Rv, but not attenuated H37Ra, causes significant mitochondrial inner membrane disruption in macrophages leading to necrosis. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950). 2006;176(6):3707-16. Epub 2006/03/07.
Gutierrez-Pabello JA, McMurray DN, Adams LG. Upregulation of thymosin beta- 10 by Mycobacterium bovis infection of bovine macrophages is associated with apoptosis. Infection and immunity. 2002;70(4):2121-7. Epub 2002/03/16.
Vega-Manriquez X, Lopez-Vidal Y, Moran J, Adams LG, Gutierrez-Pabello JA. Apoptosis-inducing factor participation in bovine macrophage Mycobacteri¬um bovis-induced caspase-independent cell death. Infection and immunity. 2007;75(3):1223-8. Epub 2006/12/13. doi: 10.1128/iai.01047-06.
Fifis T, Costopoulos C, Radford AJ, Bacic A, Wood PR. Purification and character¬ization of major antigens from a Mycobacterium bovis culture filtrate. Infection and immunity. 1991;59(3):800-7.
Flores-Villalva S, Rogriguez-Hernandez E, Rubio-Venegas Y, Canto-Alarcon JG, Milian-Suazo F. What Can Proteomics Tell Us about Tuberculosis? Journal of mi¬crobiology and biotechnology. 2015;25(8):1181-94. Epub 2015/03/05. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1502.02008.
Ciaramella A, Martino A, Cicconi R, Colizzi V, Fraziano M. Mycobacterial 19-kDa lipoprotein mediates Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced apoptosis in mono¬cytes/macrophages at early stages of infection. Cell death and differentiation. 2000;7(12):1270-2. Epub 2001/03/29. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400761.
Choi HH, Shin DM, Kang G, Kim KH, Park JB, Hur GM, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress response is involved in Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein ESAT-6-mediated apoptosis. FEBS letters. 2010;584(11):2445-54. Epub 2010/04/27. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.04.050.
Basu S, Pathak SK, Banerjee A, Pathak S, Bhattacharyya A, Yang Z, et al. Exe¬cution of macrophage apoptosis by PE_PGRS33 of Mycobacterium tubercu¬losis is mediated by Toll-like receptor 2-dependent release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2007;282(2):1039-50. Epub 2006/11/11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M604379200.
Sanchez A, Espinosa P, Esparza MA, Colon M, Bernal G, Mancilla R. Mycobacte¬rium tuberculosis 38-kDa lipoprotein is apoptogenic for human monocyte-de¬rived macrophages. Scandinavian journal of immunology. 2009;69(1):20-8. Epub 2009/01/15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2008.02193.x.
Sohn H, Kim JS, Shin SJ, Kim K, Won CJ, Kim WS, et al. Targeting of Myco¬bacterium tuberculosis heparin-binding hemagglutinin to mitochondria in mac¬rophages. PLoS pathogens. 2011;7(12):e1002435. Epub 2011/12/17. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002435.
Bulut Y, Michelsen KS, Hayrapetian L, Naiki Y, Spallek R, Singh M, et al. Myco¬bacterium tuberculosis heat shock proteins use diverse Toll-like receptor path¬ways to activate pro-inflammatory signals. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2005;280(22):20961-7. Epub 2005/04/06. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411379200.
Anand PK, Anand E, Bleck CK, Anes E, Griffiths G. Exosomal Hsp70 induces a pro-inflammatory response to foreign particles including mycobacteria. PloS one. 2010;5(4):e10136. Epub 2010/04/21. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010136.
Broker LE, Kruyt FA, Giaccone G. Cell death independent of caspases: a review. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Can¬cer Research. 2005;11(9):3155-62. Epub 2005/05/04. doi: 10.1158/1078- 0432.ccr-04-2223.
License

Veterinaria México OA por Facultad de Medicina Veterinaria y Zootecnia de la Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México se distribuye bajo una Licencia Creative Commons Atribución 4.0 Internacional.
Basada en una obra en http://www.revistas.unam.mx
- Todos los artículos en Veterinaria México OA se publican bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento 4.0 Unported (CC-BY 4.0). Con esta licencia, los autores retienen el derecho de autor, pero permiten a cualquier usuario compartir, copiar, distribuir, transmitir, adaptar y hacer uso comercial de la obra sin necesidad de proporcionar un permiso adicional, siempre y cuando se otorgue el debido reconocimiento al autor o fuente original.
- Al utilizar esta licencia, los artículos en Veterinaria México OA cubren o exceden todos los requisitos fundacionales e institucionales para ser considerados de Acceso Abierto.
- Los autores no pueden utilizar material protegido por derechos de autor en su artículo a menos que ese material esté también disponible bajo una licencia igualmente generosa.